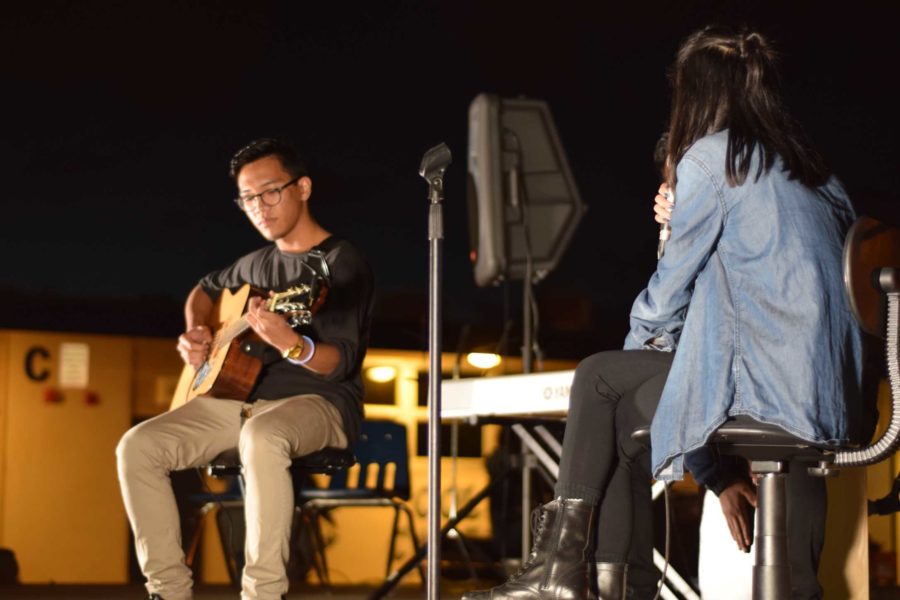
Hurricane Florence Sweeps Through The Carolinas
CONWAY, SC – SEPTEMBER 26: A home is inundated by floodwaters caused by Hurricane Florence near the Crabtree Swamp on September 26, 2018 in Conway, South Carolina. Nearly two weeks after making landfall in North Carolina, river flooding continues in northeastern South Carolina. (Photo by Sean Rayford/Getty Images) Photo provided by CNN
Gusty winds and a storm surge hit the East Coast on Sept. 1, causing damage to over 50,000 homes in North and South Carolina.
The hurricane, now named Florence, emerged from a strong tropical wave that swept over the west coast of Africa on Aug. 30, and soon transformed into a hurricane near Cape Verde. On Sept. 7, Florence was down-graded to a tropical storm, but it soon regained its strength a couple days later.
The storm was classified as a category four hurricane with powerful winds and intense rainfall. Over 34 inches of rain fell since the hurricane hit. Thousands of people were forced to evacuate and the death toll continues to climb as many still remain in shelters. Residents affected by the hurricane have been relying on coal-fired utilities due to power outages.
Farmers and livestock owners in North Carolina could potentially face $1.1 billion in agricultural damage. Hurricane Florence hit the Carolinas at the beginning of fall harvest, resulting in major crop damage. The majority of the agricultural losses will be among the farmers who cultivate crops such as corn, tobacco, and soybeans. A similar storm, Hurricane Matthew, hit the East Coast two years ago and caused an estimated $400 million in agricultural destruction.
Since the hurricane dissipated, the effects of Florence started to become apparent. Due to the intense rainfall and floods, the population of mosquitoes has risen, which could cause an influx in illnesses such as encephalitis. North Carolina has debris and organic matter littering cities. Residents have been advised to stay away from coastal areas to avoid contamination that could lead to diseases and infections such as rashes, hepatitis, and respiratory issues.

Hey there! My name is Francis, but you can call me Francis and I'm a Junior here at Cam High. This is my first year in the Stinger and I am excited to...











































































![Senior Ditch Day... Relaxation or Truancy? [Video]](https://achsstinger.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/IMG_7119-900x599.jpg)
![Heavy Rain Hits Cam High [video]](https://achsstinger.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/maxresdefault-900x506.jpg)



